자바/지네릭스
지네릭스의 전반적 개념(2)
백_곰
2022. 5. 11. 11:33
5. 제한된 지네릭 클래스
- 타입 문자로 사용할 타입을 명시하면 한 종류의 타입만 저장할 수 있도록 제한할 수는 있지만,
그래도 여전히 아래의 코드처럼 모든 종류의 타입을 저장할 수 있다는 것에는 변함이 없다.
FruitBox<Toy> fruitBox = new FruitBox<Toy>();
fruitBox.add(new Toy());
// 과일상자에 장난감을 담을 수 있다?
( 이러한 것을 해결하기 위해서는 class 이름 뒤에 아래와 같이 지네릭 타입을 주면 된다. )
class FruitBox<T extends Fruit>{ // Fruit의 자손만 타입으로 지정가능
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
...
}
public class Exercise002{
public static void main(String[] args){
FruitBox<Apple> appleBox = new FruitBox<Apple>()
// 컴파일 정상
FruitBox<Toy> toyBox = new FruitBox<Toy>();
// 에러 발생
}
}
5-1. 제한된 지네릭 클래스를 이해하기 위한 예제(1)
: 클래스 이름 뒤에 지네릭을 지정하여 구현한 예제이다.
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Exercise002 {
public static void main(String[] args){
FruitBox2<Fruit2> FruitBox2 = new FruitBox2<Fruit2>();
FruitBox2<Apple2> AppleBox2 = new FruitBox2<Apple2>();
FruitBox2<Grape2> grapeBox2 = new FruitBox2<Grape2>();
// FruitBox2<Grape> grapeBox2 = new Fruit2Box2<Apple2>(); // 에러. 타입 불일치
// FruitBox2<Toy> toyBox2 = new Fruit2Box2<Toy>(); // 에러.
FruitBox2.add(new Fruit2());
FruitBox2.add(new Apple2());
FruitBox2.add(new Grape2());
AppleBox2.add(new Apple2());
// AppleBox2.add(new Grape()); // 에러. Grape는 Apple2의 자손이 아님
grapeBox2.add(new Grape2());
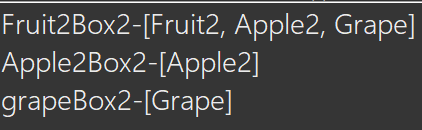
System.out.println("Fruit2Box2-"+FruitBox2);
System.out.println("Apple2Box2-"+AppleBox2);
System.out.println("grapeBox2-"+grapeBox2);
}
}
interface Eatable {}
class Fruit2 implements Eatable {
public String toString() { return "Fruit2";}
}
class Apple2 extends Fruit2 { public String toString() { return "Apple2";}}
class Grape2 extends Fruit2 { public String toString() { return "Grape";}}
class Toy2 { public String toString() { return "Toy" ;}}
class FruitBox2<T extends Fruit2 & Eatable> extends Box2<T> {}
class Box2<T> {
ArrayList<T> list = new ArrayList<T>();
void add(T item) { list.add(item); }
T get(int i) { return list.get(i); }
int size() { return list.size(); }
public String toString() { return list.toString();}
}